Aggression in Children and How to Handle it
/Aggression- how to decrease behaviors
By Patience Domowski, LCSW
Aggression in children is really difficult. From yelling to hitting, its very disruptive and sometimes even dangerous. Especially as the child gets older it becomes more of a safety concern. A 3 yr old hitting a parent is not that big of a problem, but a 13 yr old could really hurt someone.
To solve this problem we need to figure out why it is happening. Here are some possible causes:
-Child cannot manage their emotions (needs coping strategies), gets easily angry, anxious, frustrated, etc
-Child cannot effectively communicate (hasn't developed full speech due to age or speech delay, or autism)
-Child has a mental health diagnosis (autism, bipolar, ODD, …)
-Child has observed and copied aggression from older siblings, parents, violent TV
-Child is very impulsive (can’t stop and control themselves)
-Child has discovered that this gets them what they want from others (example: if they hit then people leave them alone, if they yell then dad gives in, etc)
-Child gets attention from their behavior (even though it is negative, some children still want this attention).
-Other reasons…
For some children there may be a combination of reasons. Sometimes the reason is easy to discover but other times it may be more complicated. Collecting data (writing down the behaviors and what happened before and after) and doing an FBA (Functional Behavior Analysis) can be helpful. Ask your child’s teacher or behavioral therapist about how to do one if it is difficult to figure out the ‘why’ for the behaviors.
To correct the behavior we want to teach the child a combination of better coping strategies and a more effective way to get what they want.
For example: if they get angry easily when their sibling takes their toy we want to teach them to calm down, and also the skill of asking for the toy nicely, or asking a parent for help. If the child wants attention then teaching the child a more appropriate way such as saying “Mom, play with me!” instead of hitting would be helpful. Also the parent should ignore the inappropriate behavior until the child does the expected response.
If the child is copying others aggressive behavior- whether in person or on TV shows/games/ etc it is important to limit this exposure. If the parents are showing aggression such as yelling and hitting children, then it's likely the child will copy this as well. If the parents can try to be more patient and handle their frustrations in a more appropriate coping way, this can greatly help the child. Parents may want to seek therapy on their own, or try anger management groups, or even medication to help, if they are really struggling with depression for example. If older siblings are exhibiting aggression it is helpful to try to get them some more help and teaching the younger child to not copy those behaviors. If the child is watching violent TV shows, movies, video games, eliminate or at least reduce the frequency the child is exposed to that. If the child resists, explain that if they reduce their aggression they can slowly return to those games/shows etc. Pay attention to the ratings on games and shows however and the child’s age.
For cursing- if it’s in conjunction with anger and aggression, use same strategies already listed to teaching better coping behaviors, but besides that mostly ignore it, or teach a silly replacement word “peanut butter jelly sticks!” The more attention you give the curse word, the more powerful they become. You can tell them not to say that word and maybe even why, and if necessary punish for it, but if you make a huge deal about it (such as yelling and lecturing) it will likely make it worse. Also make sure parents and older siblings are refraining from using those words completely. Even if parents tell child not to say a word, if they are saying it themselves, the child will still learn it and repeat it. With any behavior, parents need to model good behavior and not to do anything they would not want their child to do (for the most part). Sometimes an old fashioned ‘swear jar’ is helpful. The person that says the bad word is ‘fined’ and has to pay real money into the jar.When the jar is full some families will use it for a fun activity, sometimes the money would go to the non-swearing person, or maybe the family would donate it to a charity.
Make sure the child’s aggressive behavior is not getting them what they want. If they are hitting their sibling to get them to leave them alone, and its effective, that is going to maintain the behavior. Try to teach the sibling to respond better and quicker and teach the aggressive child to request space in a better way. If the aggressive behavior is getting them the attention or item they want from parents, parents need to try hard to not give in. Even though it makes the screaming stop now, it will just make the behavior worse the next time if you give in.
If the child has not developed appropriate speech, due to age or delays, it maybe be helpful to teach a simple hand gesture/sign language to use to communicate. Maybe a clap means ‘Can I have it?’ or a hand tap means ‘I need help’. Ask your child’s speech therapist for some ideas to figure out what will work best for your child’s speech needs.
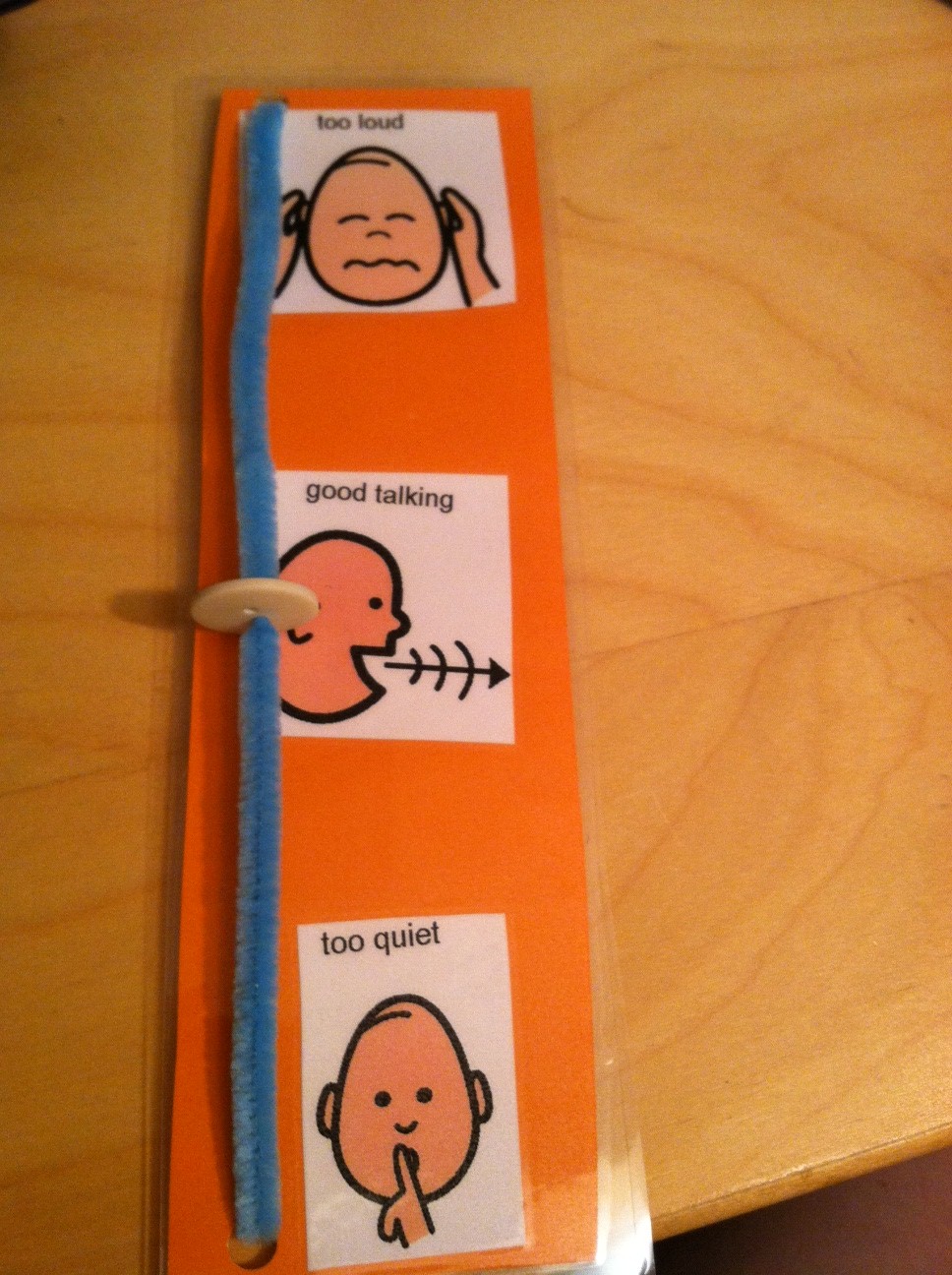
For kids who don’t have good coping strategies have them write up a list (or draw) several things they can do when they are angry and then hang the list in a well-trafficked area in the home (living room or kitchen is usually good). The list should be visible because when someone is angry they are not going to go searching for a paper in a drawer to figure out what to do. The strategies can include deep breathing, walking away/ignoring, asking parents for help, doing something fun to distract yourself, and remembering to ask nicely for things. There are many coping strategy lists that can be found online. The key is to find which ones work best for your child and to have your child identify these as well. The more the child is involved in identifying the strategies the more likely the child will use them. Also have the child act out the appropriate coping strategy when they are in a good mood, as a role play, or after they made a poor choice to reenact making a better choice.
Try giving a reward to the child for using a strategy. For example if the child takes a deep breath instead of hitting mom, or stops screaming by deciding to go chill out in their room, give them a piece of candy, access to a special toy, or extra ipad time for making a good choice. Praise your child for calming down, whether it took 10 seconds or 1 hour, immediately praise them when they are calm so they associate positive attention with calming down.
Try behavioral charts. Children are often not motivated to make a better choice internally - it’s easier for them, or not big deal for them to yell and hit versus breathe and ask nicely. But if you sweeten the deal by offering candy, toys, extra time, other privileges then they are more likely to make the better choice. Some kids will need the reinforcement reward immediately and some can wait until the end of the day or week. Think about your child’s needs and personality to figure out the immediacy of rewards. If you aren't sure how to do this seek out a behavioral therapist who is experienced in this and can help you. Once your child learns the strategies to handle their feelings more appropriately they are likely to reduce aggression and you can fade out the behavior chart, or use the rewards to target another behavior.
Sometimes if the child is so out of control and aggressive they have to be restrained. Parents can learn appropriate ways to restrain their children (ask the school, doctor, or a therapist). If the child is in danger to themselves or others it is okay to restrain them until they are calm and in control again. The police and mental health crisis workers can also be helpful in these situations. If aggression is a regular occurrence, behavioral interventions are not effective, and the behaviors are fairly severe, medication may be necessary. Talk to your child’s doctor or seek a child psychiatrist for help.
Helpful Links:
Swear Jar: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Swear_jar
Child Restraining: https://www.k-state.edu/wwparent/courses/rd/toolbox/rdtool-37.html
Causes of Aggression:
https://childmind.org/article/aggression-in-children-causes/
Handling aggressive behavior:
https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/how-to-manage-aggressive-child-behavior/
Taming Aggression and Coping for parents:
http://www.parentingscience.com/aggression-in-children.html
Anger Strategies (Other helpful blog articles)